The Cape Peninsula Fire Protection Association (CPFPA) was formed in 2002 with the aim of coordinating fire fighting activities on the Cape Peninsula mountain chain. Renowned for its scenic beauty, the Peninsula hosts two prominent world-famous landmarks, Table Mountain and the Cape of Good Hope. Contained within the south-western cape the peninsula forms part of the Cape Floral Kingdom, which comprises the unique fynbos biome. Although limited in area this kingdom has been declared one of the earth’s six plant kingdoms; with over 8700 plant species, many of these endemic and a high proportion of threatened by urban encroachment, it is an ongoing challenge to preserve our heritage.
Fynbos thrives in the winter rainfall climate of the south Western Cape, and is both fire-prone and fire dependent; studies have shown that the fynbos tracts need to burn in cycles of around twelve to twenty years to maintain the species. This vital factor underlies the rationale of the CPFPA.
The Peninsula itself is unique in that the mountainous terrain is surrounded by an extensive, highly populated urban area, and the lengthy interface between urban population and fire-prone vegetation needs complex integrated fire management. The CPFPA has been at the crux of this process in the last decade, working in conjunction with professional partners to combine scientific research with effective suppression of fires and the rehabilitation of burnt areas.
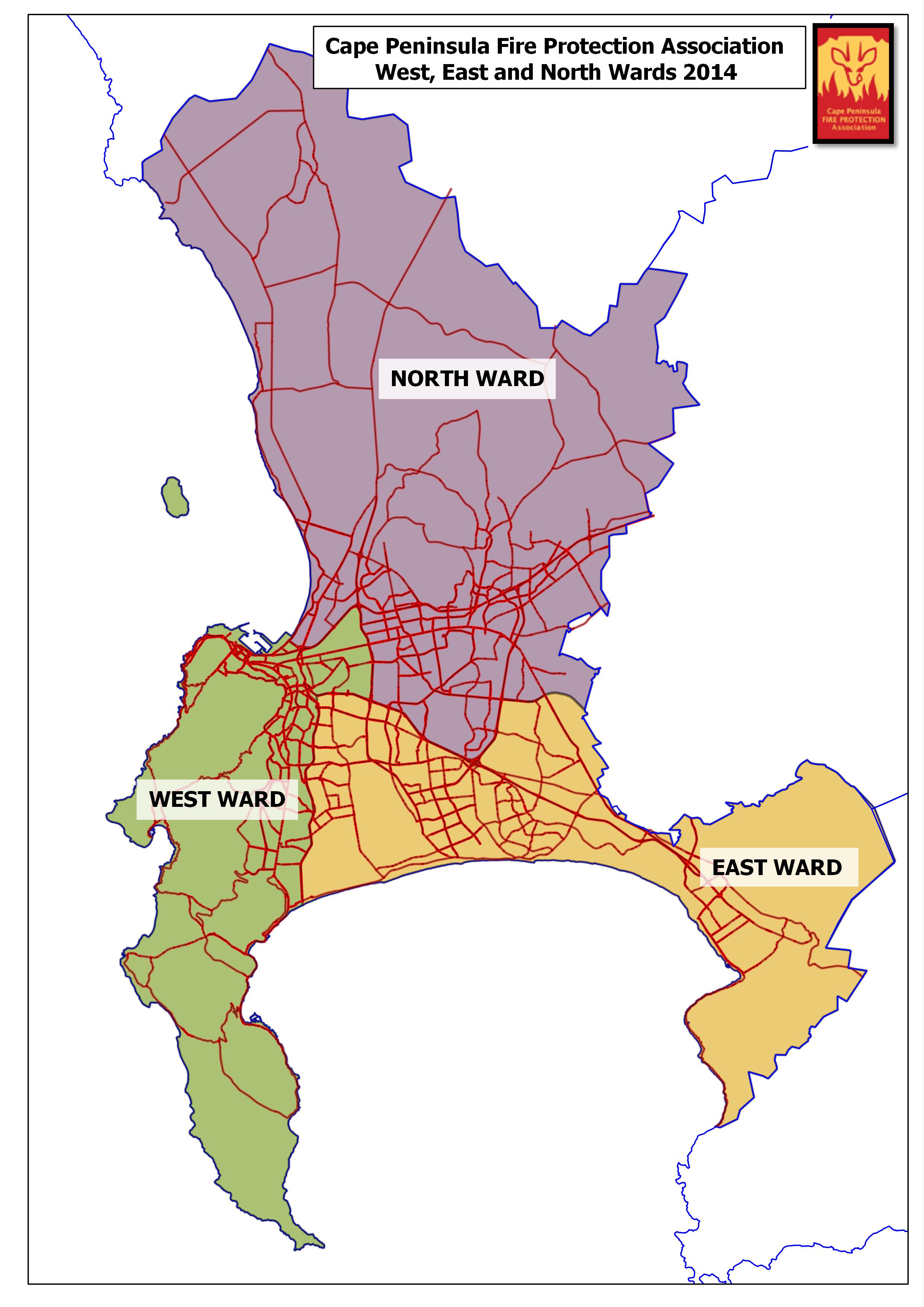
The success of the CPFPA over the years in co-ordinating fire management has led to extensive enlargement of the area under its jurisdiction. Initially limited to the area of the peninsula itself, the CPFPA now controls three ‘wards’ in the south -western cape.
The original peninsula area, the West ward, is abutted by the East ward which extends as far as the Hottentots Holland Mountains and incorporates the Gordon’s Bay/Strand/Mitchells Plain area. Included in this ward are commercial forests and the catchment area of the Steenbras Dam.
The new North Ward is linked to both East and West Wards, and extends up the West Coast, incorporating Melkbos, Koeberg, Atlantis and Mamre to the north, and areas above Durbanville and Klipheuwel to the northeast.
This has enlarged the overall area under the fire management jurisdiction of the CPFPA from 514 sq km to 2466 sq km. The challenge to the CPFPA is not only in the increased area and additional responsibility, but in the multiplicity of vegetation types that are now in consideration when wildfires threaten.
